Real-World Application
Picture this. Your construction business is booming with all projects on track. Your crew is finishing a big job for a prominent client. Unexpectedly, you receive a call that changes everything. You discover that essential tools/equipment are missing. Furthermore, you decide that you have no other choice than to put the job on pause as you contemplate the next steps.
The harsh reality is that theft is a risk in the construction industry. The National Equipment Register (NER) estimates the total value of construction equipment and tools stolen each year to be between $300 million – $1 billion. Without a doubt, theft impacts construction businesses in several ways. Some of these impacts include tool/equipment rental costs, replacement costs, fines for schedule delays, decreased productivity, increased insurance premiums, and lost time filing police reports and insurance claims.
Many solutions are available to combat theft. One solution is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology which utilizes a wireless system comprised of two components: tags and readers.
Problem Proposition
Tracking the checkout and return tools from a tool crib location. The tool crib can vary in size. Additionally, the number of tools located within the crib can vary. In all cases, the tool cribs will have limited points of egress.
Two sample cribs are defined in the following diagrams.

Objective: To know when tools are removed from the crib and who took the tool(s).
Proposed Solution
Overview
The best solution for this problem that does not require a great deal of manual operation is the incorporation of UHF RFID readers and tags. This method will allow for a hands-free system by which both assets and users can be uniquely identified.
Each asset and employee would have a unique RFID tag assigned to them. The system can then determine which is an asset and which is a worker and therefore create the assignment accordingly.
RFID Technology
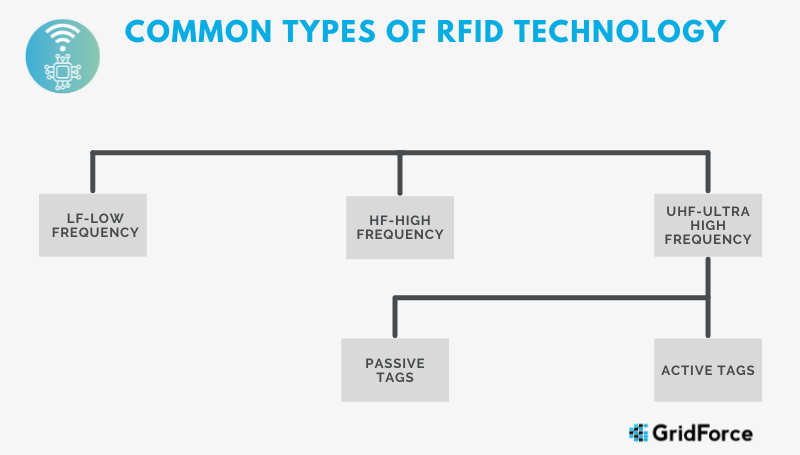
Types of RFID Technology
Several categories of RFID technologies exist. The 3 most prevalent and widely available ones include LF, HF, and UHF.
LF – or Low Frequency and HF – High-Frequency tags are commonly used in near-field applications. Examples of this include RFID dog tags and access control systems. They have relatively low data transfer rates and work in a close-coupled antenna field. Read ranges will vary from 1 – 12 inches.
UHF – or Ultra High-Frequency tags are common to medium to far-field applications. UHF tags have been adapted by Airport Terminal Baggage Tracking Systems and in the retail and logistics space. They offer higher data transfer rates and often contain user-programmable memories. Although very dependent on Tag antenna size and Reader antenna gain, read ranges of 1 inch and up to 30 feet are achievable.
For this scenario, it is recommended to use UHF RFID technologies. These systems are widely used in industrial and retail applications for tracking movement and identification of unique materials.
Types of UHF RFID Tags
UHF RFID tags are available in two “classes” of tags: Passive tags and Active tags.
Passive tags: Passive tags do not contain a battery. They get powered by the RF field generated by the RFID interrogator. These tags are the less expensive type of tags and still offer good read ranges. Real-world read ranges typically reach up to 6 feet. Passive tags will range in cost from $0.20 to $15.00.
Active Tags: Active tags do contain a battery. There are a couple of different operating scenarios for active tags. However, the main advantage is read ranges are often more than 20 feet because they actively transmit data. Since the tags must contain a battery, it is possible to find active tags that contain GPS, Dataloggers, G-Force measurement, etc. This does come with a price. Active tags are considerably larger than passive tags and do require battery replacement. Active Tags will range from $20.00 and up.
In most applications, Passive RFID tags will work well.
However, UHF RFID systems have some additional advantages in this scenario.
- Multiple Tags can be read at the same time.
- Depending on the hardware, read rates in excess of 300 tags/sec are achievable.
- Tags are available for a wide range of applications within the scenario.
- Metal-based tags
- Simple Sticker tags
- Embeddable Tags
- Harsh Environment / Chemical resistant tags.
Approach
The approach to creating a system for tracking tools would be as follows:
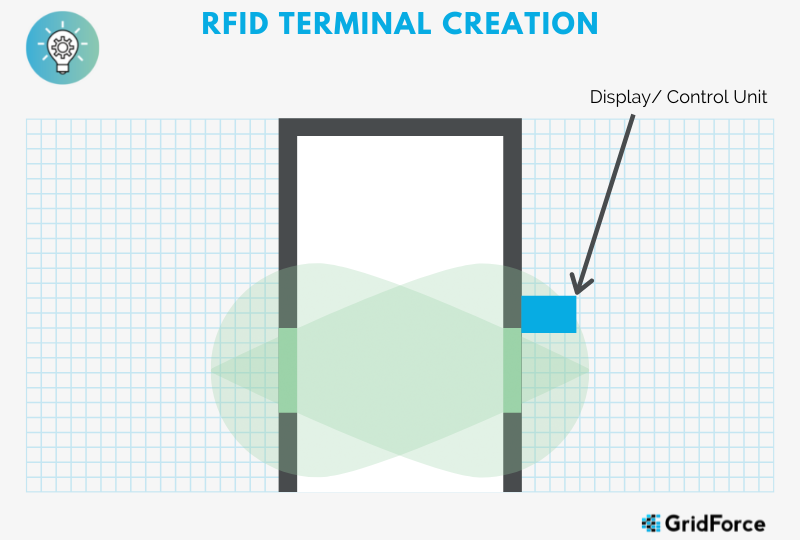
At each point of Egress, an RFID terminal would be installed. The “terminal” consists of:
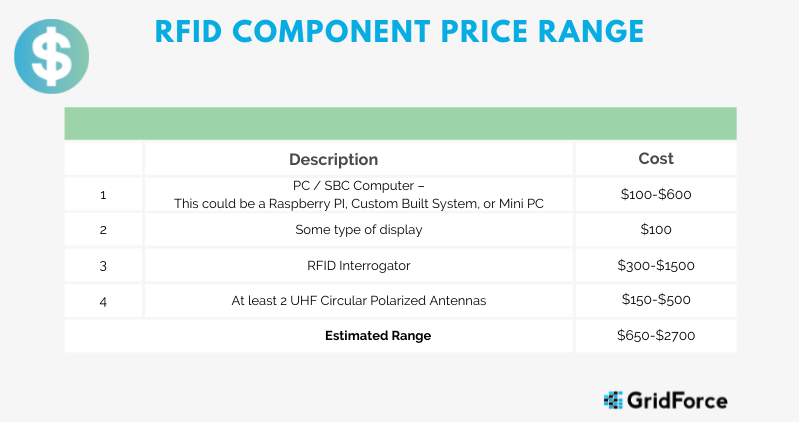
- PC / SBC Computer –
- This could be a Raspberry PI, Custom Built System, or Mini PC
- Some type of display
- RFID Interrogator
- At least 2 UHF circular Polarized Antennas on each side of the entryway. The idea is to
encapsulate the entry within the RF Field.

Each Asset gets tagged with a UHF RFID tag. Each worker also carries a UHF RFID badge. As the employee approaches the RF field, the tags activate and transmit their IDs. The system receives the ID and processes the information accordingly.
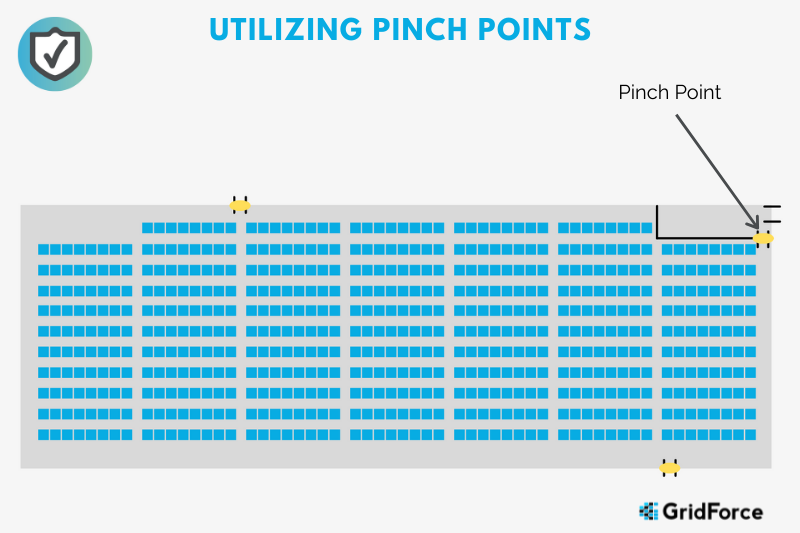
In the scenario outlined, due to the fact that the situation involves a garage bay and vehicles, it is necessary to modify the approach taken.
The trouble with egress monitoring in the case of vehicles exiting the monitoring area is that metal blocks RF energy. In most work trucks, not only is the cargo area itself usually metal, but then the workboxes, toolboxes, and carry cases are also metal. This significantly decreases the chances that the RFID system will be able to appropriately pick up tagged items enclosed in those areas.
To address this obstacle, access from the tool crib to the garage space should be limited through the use of one or multiple “pinch” points. Once this issue is resolved, monitoring will be conducted as outlined in the approach.
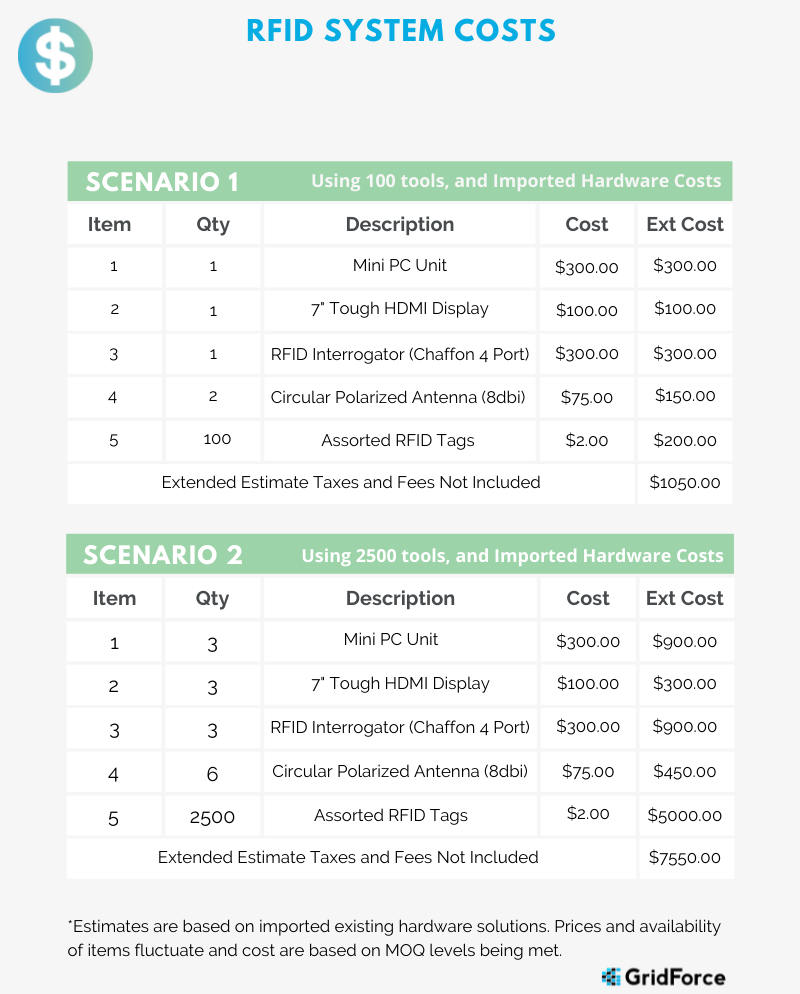
System Costs
RFID readers and antennae vary greatly in cost. Much of this depends on the differences between industry-recognized brands or generic brands. Alien Technology is a recognized leader in RFID technology. They offer an efficient high-quality industrial reader. These are one of the most expensive readers out on the market.
Summary